|
Hearing loss in Children
Studies have shown that children with permanent moderate or greater degrees of hearing loss can have significant effects on language & speech development:
|
Language & Speech Development Of Normal Hearing Children:

Newborn – 1month
- Pay attention to people's voice
- Jumps or blink to loud sound
- Smile when you talk

1-3 months
- Head will rotate in the direction of the sound
- Listen to music
- Express their emotions and needs with crying, cooing, facial expressions and body movements

4-7 months
- Turns towards voices or sounds
- Seem to like a musical toy
- Respond to the call from others
- Start babbling

8-12 months
- Listen when people talk
- Understand things like “no”, “bye bye”
- Like copying sounds

1-2 years
- Can distinguish object names and body parts
- Understand and follow simple instructions
- Listen to simple story and songs
- Usually understand nouns firstly and learn verbs later

2-3 years
- Understand and follow simple instructions
- Can differentiate common items and the name of the picture
- Find you when you call from another room
- Understand most of what you and teachers say
- Can answer simple question
- Like books, story-time and able to answer questions after being read to
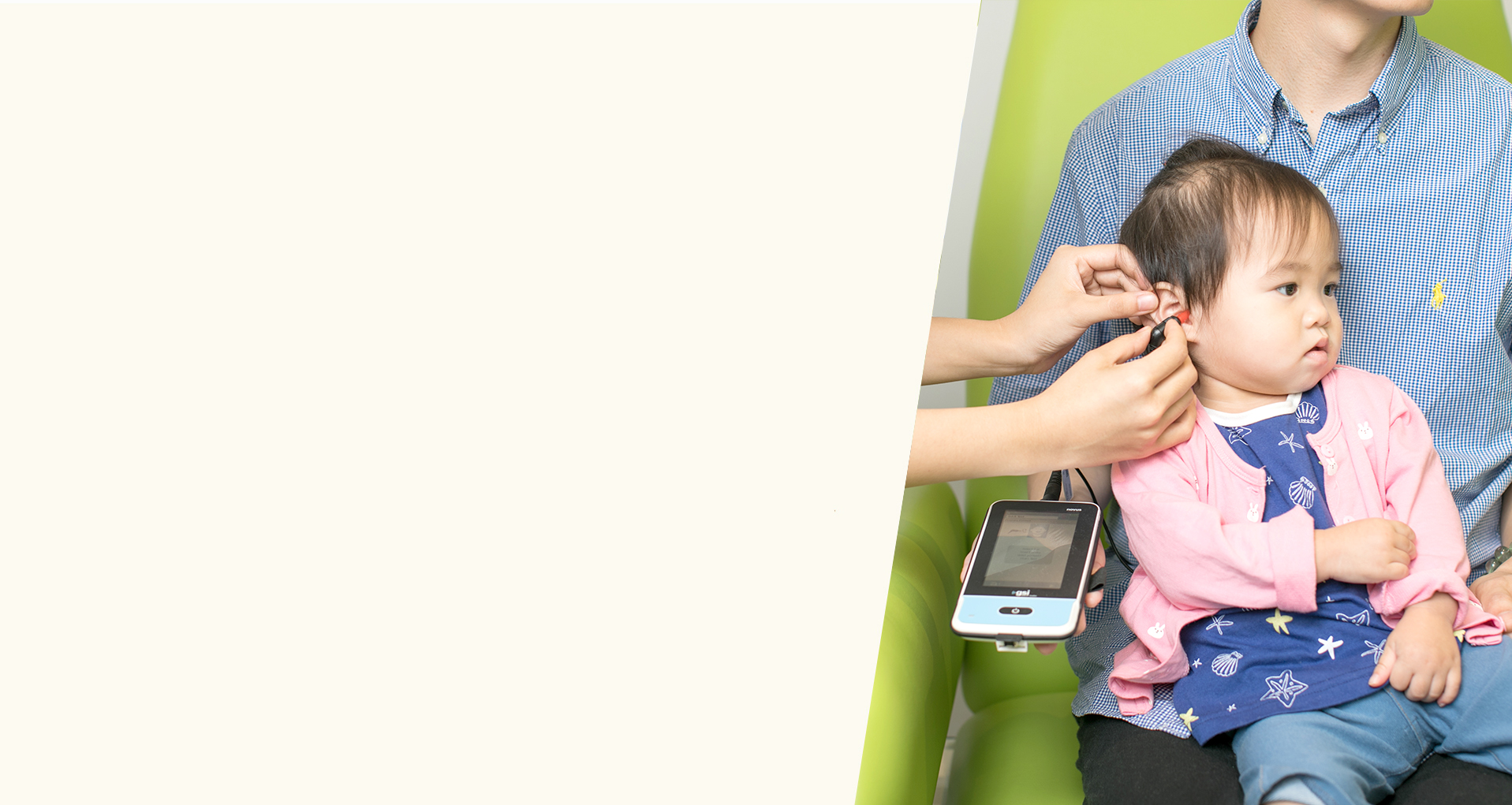
We provide the following two tests as part of the Newborn Hearing Screening service at Phonak:
Applicable: 0 to 6 months of age;
Test Time: 1 hour
Test Time: 1 hour
Automated Otoacoustic Emissions (AOAE)
OAEs are measurable sounds emitted when the cochlea is stimulated with clicks or tone stimuli. The OAEs are recorded via a probe assembly with a microphone, placed in the infant’s external ear canal. OAEs provide information about the integrity and function of the outer hair cells of the cochlea when the middle ear has been shown to be free of effusion.
Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR)
Compared with OAE, AABR technology is sensitive to auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder, and with a higher level of accuracy. It is an electrophysiological measure of neural responses to auditory stimulation. In AABR, broadband stimuli (click or CE-chirp) of a screening intensity level (e.g. 35 dB nHL) is presented to elicit neural responses from the auditory nerve to the brainstem.
We provide the following three tests that are commonly used in Newborn Diagnostic Audiological Assessment protocol:
Applicable: 0 to 12 months of age, or older child when needed;
Test Time: 2 hour
Test Time: 2 hour
Tympanometry /Impedance Audiometry
Measures of middle ear function assist in the differentiation between conductive and sensory/neural sites. The measure for detecting middle ear dysfunction in infants under 6 months of age is 1000-Hz tympanometry.
Non-Sedated Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR)
ABR aims to estimate hearing sensitivity and to identify neurological abnormalities of the auditory nerve and the auditory pathway up through the brainstem. Electrodes are placed on the head, and auditory evoked potentials in response to sounds are recorded.
Auditory Steady State Response; ASSR
ASSRs are electrophysiological responses elicited by periodically repeated auditory stimuli. The purpose of ASSR is to estimate hearing thresholds. Frequency-specific modulated tones are used in ASSR to evoke neural responses that enable estimation of thresholds and form the foundation for determining hearing aid amplification characteristics.
Our Paediatric Audiological Services provided :
Visual Reinforcement Audiometry(VRA)
Applicable: age of 6-months to 3 years old
Applicable: age of 6-months to 3 years old
Purpose:Aims to assess the hearing levels of children through providing them with visual “reward”.
Procedure:Sounds of different frequencies are presented either via headphone or sound field speakers to the child inside the sound booth. The child is conditioned to make a head turn towards the direction of sound stimuli. Slides of animation will be then presented on display monitors as a visual “reward” to reinforce the child’s responses
Procedure:Sounds of different frequencies are presented either via headphone or sound field speakers to the child inside the sound booth. The child is conditioned to make a head turn towards the direction of sound stimuli. Slides of animation will be then presented on display monitors as a visual “reward” to reinforce the child’s responses
Conditioned Play Audiometry (CPA)
Applicable: age of 2 to 5 years old
Applicable: age of 2 to 5 years old
Purpose:Aims to assess hearing levels of children through a Conditioned Play Audiometry.
Procedure:Sounds of different frequencies are presented via headphone to the children inside the sound booth. The child is conditioned to perform a task with toys when a sound is heard, such as putting a block in a box to indicate that she/ he heard the sound.
Procedure:Sounds of different frequencies are presented via headphone to the children inside the sound booth. The child is conditioned to perform a task with toys when a sound is heard, such as putting a block in a box to indicate that she/ he heard the sound.
Audiological Assessment
Applicable: above age of 6 years old
Applicable: above age of 6 years old
Include Pure Tone & Impedance Audiometry